Brief Aspects on Different Mercury Monitoring Techniques

The recent revision in environmental norms issued by MOEF made it mandatory for thermal power plants and process industries to measure mercury emission in air .Hence it is impervitive that proper understanding of mercury measurements technology and its availability in market is essential for the implementation of mercury measurement mechanism in plant
This paper makes an attempt to bring out the availability technologies and their commercial usage for mercury measurement and monitoring.
Mercury is found in environment in various distributed & different forms. Elemental mercury vapor is found in atmosphere, while inorganic & organic form of element is found in soil, water, plants & animals. Natural sources of mercury are from forest fires, volcanoes and weathering of mercury bearing rocks. However large amount of mercury gets liberated to atmosphere through various human activities like combustion of fossil fuels , incarnation of solid waste , mining etc ,
A Toxic metal mercury exists in coal. Mercury is volatized and a portion of volatized mercury is absorbed in unburnt carbon and ash, when coal is combusted.. They are captured along with particulate matter.
So, It is difficult to predict and also complicated to characterize the Mercury emissions during coal combustion. In vapor phase volatile mercury is thermodynamically stable at high combustion temperature and at low temperature major portion of mercury gas absorb into ash and oxidized compounds in flue gas and form mercury compound after reacting with mercury vapour
During the combustion, the mercury in the coal is liberated into 3 forms – particle bound mercury, elemental mercury and oxidized mercury.
Hence , to control Mercury emission first step is to measure and monitor the mercury emission and thereafter introduce mercury control mechanism to reduce the mercury emission. Various methods are used to measure mercury emission. These methods are divided into offline through manual analysis and online analysis.
Manual analysis – Wet chemical mercury testing and dry sorbent method.
Dry sorbent methods are very popular and used for measuring mercury concentrations and speciation. Wet chemical method (Method 20 US Environmental protection agency (USEPA )) is a relatively complex method and also costly . USEPA has developed a mobile mercury monitor toolkit based on Sorbent trap popularly known as Tool kit in Large TPP. These are now generally used by regulators and the researchers. In sorbent trap sampling system, mercury is collected inside a trap that is filled with a sorbent medium such as iodated carbon. The collected sample is analyzed using traditional wet chemical methods or by thermal decomposition/ direct combustion. This OH method (Ontario Hydro method) is a choice in measuring mercury concentration and speciation.
Methodology for collecting sample
- Sampling probe with pair of sorbent traps installed in the stack.
- Flue gas is pulled through the sorbent traps which collect mercury from the gas
- Each sorbent trap has 2 to 3 sections. 1st section quantitatively captures mercury and 2nd section is used for breakthrough calculation and 3rd section commonly used for compliance reporting since it contains known amount of mercury.
- Each sorbent section is individually emptied into Quartz ladle and analyzed in analyzer. Analysis takes usually around 90 seconds.
This system involves continuous and repetitive stack sampling, using paired sorbent traps in subsequent analysis as time integrated samples. This system can be a primary system for compliance monitoring and as back up during CEMS maintenance & verification of performance.
ONLINE ANALYSIS
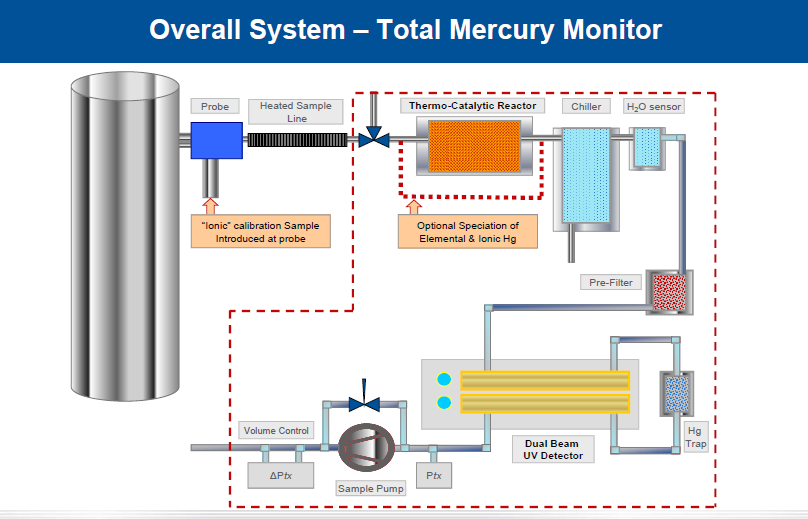
Online CEMS is used for real time monitoring and analysis.
The popular advanced techniques used are
- Cold vapor atomic absorption spectrometry (CVAAS)
- Cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (CVAFS)
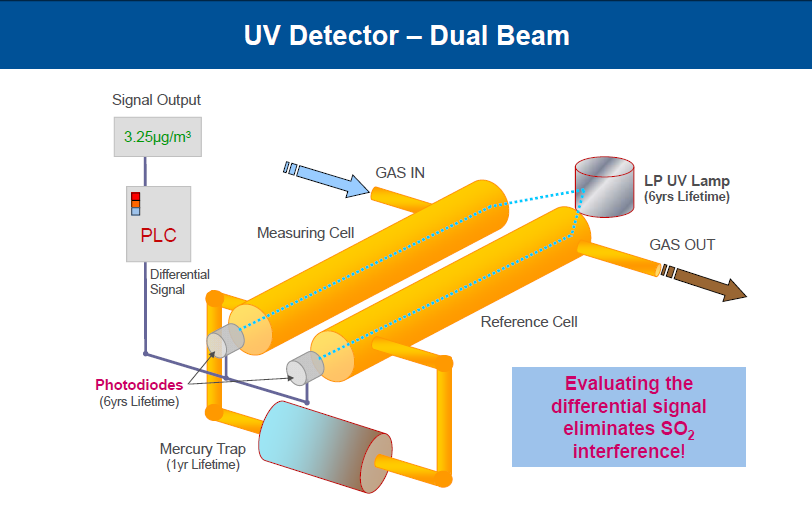
The working principle of above online mercury monitoring is similar to other flue gas monitoring emission systems. Objects to be analyzed are taken by sampler from flue gas .The interferential components available in sample gas such as HCI, SO2, SO3, andother acidic gases are removed before going to detector
Cold Vapor Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (CVAAS)
It is widely accepted methods for determining mercury i.e total mercury content. Mercury is reduced to elemental form for by using Tin Chloride or Sodium borohydroide From solution, vapor mercury is purged by air, nitrogen or argon carrier gas. After it passes through gas liquid separately, it is led into optical path of atomic absorption spectrometer.
These analyzers use a electrode less discharge lamp EDL as light source which is driven by high frequency. Extremely narrow band width emission lines are generated by lamp which is congruent with mercury atom absorption lines .
CVAAS is primary technique for analyzing mercury. These instruments have peristaltic pump that transports sample & stannous chloride separately into gas liquid , where pure dry gas (argon) stream is introduced into liquid mixture to release mercury vapour . Mercury shall be carried by dry argon gas in vapour phase through dryer and into atomic absorption optical cell. In absorption cell, the elemental mercury will absorb the light at 253.7 nm in logarithm which is proportion to its actual concentration of the sample.
Cold Vapor Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy (CVAFS)
These mercury analysis include sub ppt detection limits and much wider dynamic range can be achieved. CVAFS analyzer are available with 2 configurations – one which employs single atomic fluorescence and other which employs gold amalgamation system to pre concentrated mercury. The detection limit for only fluorescence approach is 0.2 ppt whereas method using pre-concentration approach with fluorescence detection is low as 0.02 ppt.
The sample is introduced by peristaltic pump and stannous chloride into gas liquid separator where pure dry argon gas stream is bubbled through a mixture to release mercury vapor. This technique uses unique characteristic of mercury that allows measurement at room temperature.
The mercury is transported in carrier gas through a dryer and then to a valve which selects between fluorescence & pre concentration approach. In the detector mercury vapor absorbs 254.7 nm and fluorescence at the same wavelength. Fluorescence signal is the measurement at 90 deg to incident beam to minimize scatter from excitation source. The intensity of the fluorescence light is directly proportional to the concentration of mercury.
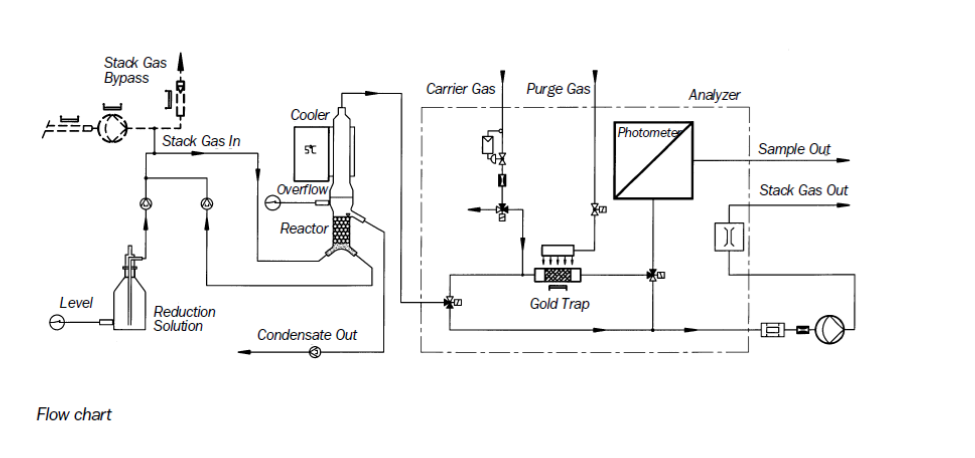
Typical flow diagram of CVAAS monitor
Courtesy- Sick instruments
Courtesy- Sick instruments
The Gas flow path consists of strong bypass stream from which for a sample preparation a small partial stream is extracted by a built in gas transfer pump. The 2nd pump extracts the partial stream and sends it to reduction step & amalgamation unit. All the components in contact with gas are heated electrically to high temperature.
Reduction
Mercury chloride compounds are reduced to elemental mercury by wet chemical reduction process with SnCl2 solution within reduction vessel. Excess condensate is removed by peristaltic pumps & feed in reductant solution. This sampling gas is conducted into the gold trap after processing.
Amalgamation
During this process a defined sample gas volume is conducted through gold trap, so metallic mercury forms an amalgam with gold. Gold trap is heated electrically and in collection phase they are released and later transported through photometer cell by inert carrier stream of gas. In this amalgamation technique interferences of other flue gas components are avoided since analyzer is in contact with mercury & carrier gas
Photometric measurement
Atomic absorption spectrometry is used to measure mercury. Single beam photometer with Hg discharge lamp, photodiode detector, quartz cell & assembly is thermo-stated. So high stability measurement is ensured due to baseline correction automatically.
For Reference courtesy- Durag
The continuous mercury monitors shall meet these following needs:
- The analyzers results indicate mercury emission and healthiness of Air pollution control devices (APCD).
- The analyzers shall distinguish the various chemical form of mercury
- The analyzer result can be used to control feed rate of the process responsible for mercury emission
- The analyzers results can be used to check and ensure compliance to regulatory norms
India has already revised to more stringent emissions norms to embark as the road map of improving energy efficiency and reduce emissions. However, it is imperative that following mercury control strategies to be taken in current scenario in Indian context to improve & reduce emissions.
The broad control strategies for controlling mercury emissions
- To improve plant efficiency by modernization of plant equipment and coal treatment technologies.
- To improve air pollution Equipment like ESP, FGD & SCR.
- To install dedicated mercury removal technologies like sorbent injection & multipollutant technologies.
Conclusion
As could be seen, both offline and online measurement techniques are available for mercury measurement & monitoring. Application for offline and online system would depend upon the extent of mercury emission expected from particular industry, severity of its impact on environmental and prevailing environmental regulations.