Importance of Surge-Absorbing Circuits and Impact of Interposing Relay Reverse Polarity Connections in DC Circuit
In industrial automation applications, ‘Interposing relay’ is useful. Interposing relay is a general-purpose relay that provides isolation between two hardware circuits. Interposing relay encased with a coil and bifurcated contacts. The coil of the interposing relay is energised by AC/DC power which activates contacts that are used to trigger another hardware circuit.
If the two systems have different voltage ratings, then a DC relay (controlled by PLC/ DCS) can turn on and off a device of higher power rating and voltage requirement.
If isolation is required between two systems for safety/protection purposes or if two systems are functionally isolated, it is preferred that no disturbance propagates from one to another. Then the use of an interposing relay is the best way to provide the solution by providing isolation in between.
While using an interposing relay, coil surge is an important component to protect the relay coil from reverse voltage generated.
Functional Description of Surge-Absorbing Circuits:
When a relay is turned OFF, a large reverse voltage is generated momentarily as per the characteristic of the coil. To fix this problem, surge-absorbing circuits are introduced in the relay to drain the generated large reverse voltage. Refer comparison of reverse voltage between the circuit with coil surge and without coil surge in Figure 1 for a 24 V DC circuit and Figure 2 for a 200 V AC circuit.
When contacts are used for input, reverse voltage creates noise and produces arching. Use of surge-absorbing circuits, the noise effect can be prevented and can minimise carbides produced by arching at the contact point.
When semiconductor components (e.g. transistors) are used for input, relays may break down due to generated reverse voltage. The use of a surge-absorbing circuit is a good solution to avoid this.
A built-in surge-absorbing diode may be present in some relays (for DC coils). We can also externally install these diodes.
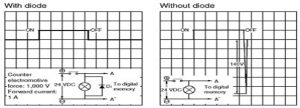
Figure-1: Reverse Voltage Comparison in a 24 VDC Circuit
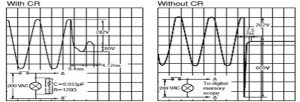
Figure 2: Comparison of Reverse Voltage in a 200-VAC Circuit
Impact of Reverse Polarity Connections in DC Circuit:
If the relay coil (with a surge-absorbing diode) is connected in reverse polarity, the surge absorption may cause a high current flow through the diode. Refer to Figure 3 for a schematic diagram of an interposing relay with a surge coil and Figure 4 for the reverse current flow in case of reverse polarity connection. If the current is greater than the current the power source can supply, it can damage the power source and the other components that are in series with the circuit. Reverse polarity may lead to the failure of the channel of the PLC/DCS digital output card or may cause the failure of the PLC/DCS digital output card itself if proper isolation/protection is not considered in the design or available protection is not functioning efficiently.
It is advisable to provide proper protection at the panel terminal and the DO card channel to avoid such failure due to reverse polarity connection.
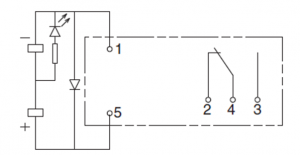
Figure 3: Schematic Diagram of an Interposing Relay With Surge-Absorbing Diode
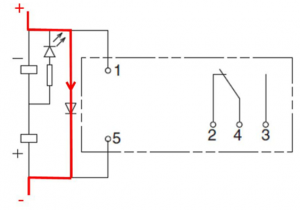
Figure-3: Schematic Diagram for Current Flow in Case of Reverse Polarity Connection
Reference:
- Catalogue of general-purpose relay
- OMRON website https://www.ia.omron.com
- OMRON Technical support team communication





