Microgrid
Microgrid is an emerging concept, which has gained significant attention and popularity in the power industry owing to its contribution to improvements in efficiency, reliability, resilience and independence over the traditional utility grid.
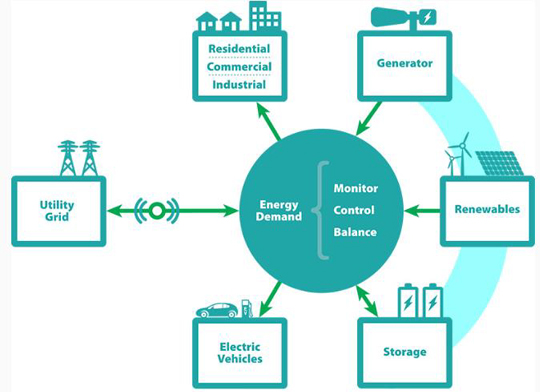
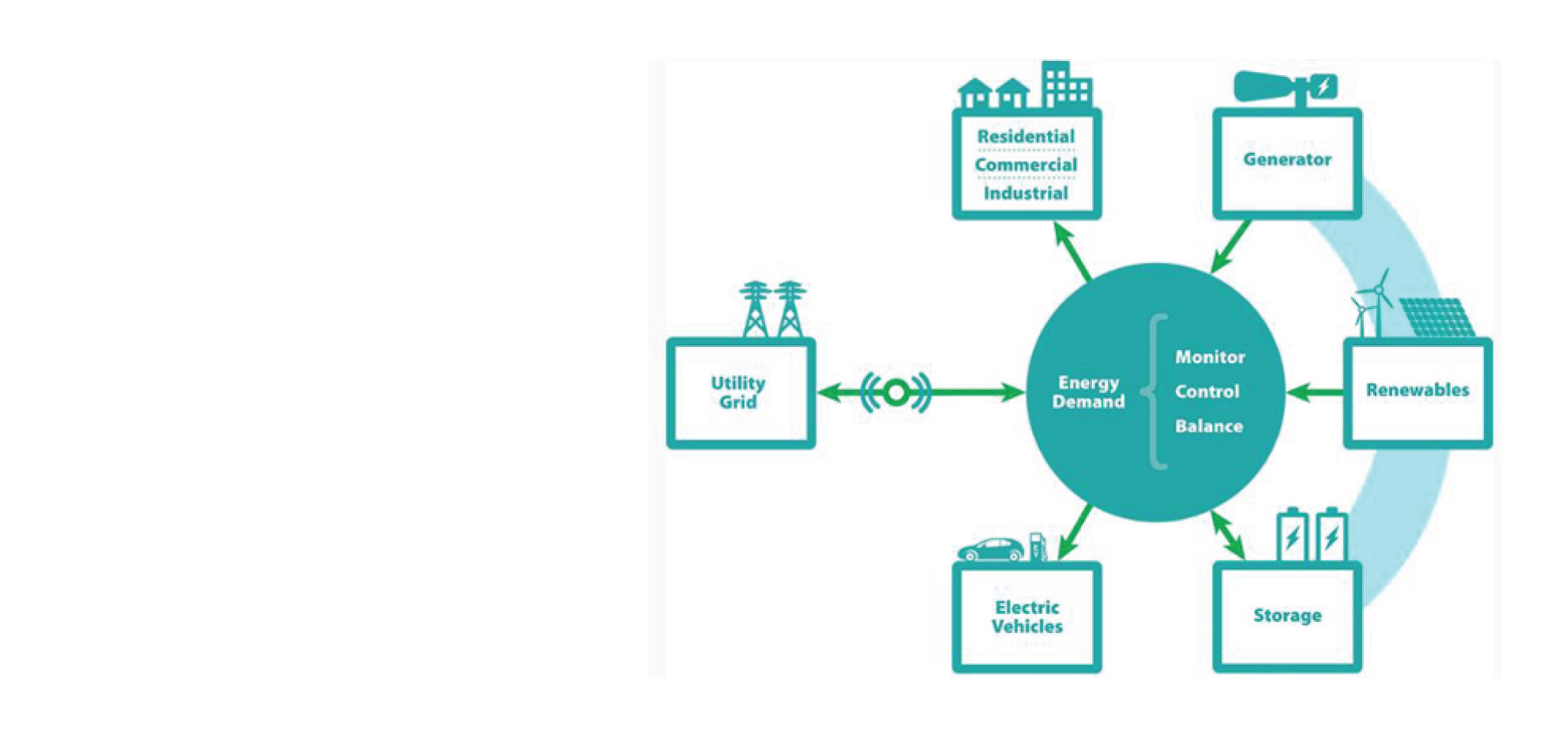
A Microgrid is a much smaller version of the centralized utility grid comprising group of interconnected loads, distributed energy resources, energy storage devices, controller and high-speed communication system. Distributed energy sources include fossil or biomass-fired small-scale combined heat and power (CHP), photovoltaic modules (PV), small wind turbines, mini-hydro, diesel generators, etc. Micro grid often uses renewable energy as one of the energy source and battery as energy storage.
As per US Department of Energy , “A microgrid is a group of interconnected loads and distributed energy resources within clearly defined electrical boundaries that acts as a single controllable entity with respect to the grid. A microgrid can connect and disconnect from the grid to enable it to operate in both grid-connected or island-mode”
Based on the grid interface, Microgrid is broadly classified as grid connected microgrid and remote microgrid.
Grid Connected Microgrid – A grid connected microgrid have multiple generators with sophisticated control system. Few examples of this type of microgrid are military microgrid, large campus microgrid, utility microgrid and community microgrid. Grid connected microgrid can either operate in connection with the central grid or islanded using their own internal generating sources.
Remote Microgrids – Remote microgrids are operated islanded without grid connections. They operate independently on their own generating sources. These are generally found on islands or isolated areas.
A micro grid can generate, distribute and regulate the electricity to its local consumers or import/export power to the grid through micro grid controllers. Microgrid controller plays a significant role in governing the overall performance of the system. Some of the key functionalities of advanced microgrid controller are:
- It communicates with various electrical devices in the microgrid
- Control and monitor all the interconnected loads and generation sources
- decides” at any given moment which energy source is most advantageous based on energy pricing and resource availability
- frequency and voltage control
- Demand management
- Spinning reserve management
- Grid connected to islanding transition and vice versa.
- Feeder management
- Renewable energy maximisation and stabilisation
The microgrid controllers are of two types; centralised or distributed. In centralised system, a central master controller will control all the elements of the microgrid and is responsible for maximisation of the output and optimisation of the operation. The drawbacks of centralised controller are i) expensive in case of large system because of large hardware and requirement of redundant controller ii)scalability and expansion is complex, iii) system maintenance requires complete shutdown, iv) diagnostics is complex due to complex algorithm and building blocks.
In distributed control system, each element is provided with a local controller with peer to peer communication. The advantages of distributed controller system are i) failure of one controller does not bring the total system down, ii) scalable and extendable, iii) economic solution especially for large systems iv) because of modularity, up-gradation is easy. Disadvantages of distributed system are i) less efficient, ii) output performance is less when compared to centralised system and iii) inherent network latency.
The potential application areas for Microgrid include:
– Remote locations and islands
– Campuses (Townships, University Campus and colleges, Software Parks, etc)
– Smart cities
– Industries with critical processes and power quality requirements
– Mining industries
– Distribution utilities
Microgrid implementation involves various challenges such as
– Clear understanding and accommodating unique operating characteristics of various generation sources.
– Managing and prioritizing power requirements
– Minimising initial investment and operating cost by identifying exact system needs
– To minimise fossil fuel generation and maximise the generation from renewable
– Identifying critical loads for operating under islanding mode
– Fault studies and analysis to address on the protection of generation system and subsystem
– Cyber security when serving for government applications, defence or any critical facilities
Tata Consulting Engineers Ltd (TCE) can offer full-fledged engineering services to the Industry/Utilities on microgrid. The services include preparation of feasibility studies, selection of energy sources based on the application and demand requirement, studies to maximise the renewable energy sources, selection of battery energy storage technology and optimum sizing of the battery capacity, basic and detailed design and engineering of complete Microgrid Project and its integration with power grid. The services would also include procurement assistance, Vendor drawing/document reviews, factory/site inspection and construction and commissioning supervision.